Are you passionate about music production but struggling to get that perfect bass sound? If your subwoofers aren’t calibrated correctly, your mixes might end up sounding flat or unbalanced.
Properly calibrated subwoofers can transform your music, giving it depth and clarity that captivates listeners. You’ll discover simple yet effective techniques to fine-tune your subwoofers for that flawless sound. Imagine the satisfaction of hearing your music exactly as you intended.
Ready to elevate your music production skills? Let’s dive in and unlock the full potential of your sound system!

Credit: www.theaterseatstore.com
Choosing The Right Subwoofer
Choosing the right subwoofer is key for music production. It helps you hear low bass sounds clearly.
Good bass response improves your mixing and mastering process.
Types Of Subwoofers
There are three main types of subwoofers: sealed, ported, and bandpass. Each type affects sound quality differently.
- Sealed subwoofers give tight, accurate bass.
- Ported subwoofers produce louder bass with more boom.
- Bandpass subwoofers offer high efficiency but less accuracy.
Size And Power Considerations
Subwoofer size affects bass depth and volume. Larger sizes give deeper bass.
| Size (inches) | Best Use | Power Range (Watts) |
| 8-10 | Small rooms, tight bass | 50-150 |
| 12 | Medium rooms, balanced bass | 150-300 |
| 15+ | Large rooms, deep bass | 300+ |
Choose a power rating that matches your room size and listening level.
Placement Options
Where you place the subwoofer changes how bass sounds in your room. Try different spots to find the best sound.
- Place near a wall for stronger bass.
- Avoid corners to reduce boominess.
- Keep some space from the floor for cleaner sound.
- Test placement by playing bass-heavy music tracks.
Setting Up Your Room
Calibrating subwoofers starts with your room setup. The room changes how bass sounds. A good setup helps you hear true bass tones.
Small changes in the room can improve your music production. Focus on room acoustics, subwoofer placement, and reducing unwanted sounds.
Room Acoustics Impact
The shape and size of your room affect bass frequencies. Hard surfaces reflect sound and create echoes. Soft surfaces absorb sound and reduce reflections.
Rooms with poor acoustics cause bass to sound boomy or weak. Treat your room with materials like foam or bass traps to control sound waves.
Positioning For Best Bass Response
Place your subwoofer where bass sounds clear and balanced. Avoid corners if bass feels too loud or muddy. Try different spots near your main speakers.
Listen carefully while moving the subwoofer. The best spot often is near the front wall but not exactly in the corner.
- Start with the subwoofer near the front wall
- Move it slightly away from corners
- Test bass at your listening position
- Choose the spot with smooth, even bass
Minimizing Reflections And Resonance
Reflections and resonance cause bass to sound unclear. Use soft materials on walls and floors to reduce echoes. Bass traps help control low frequencies.
Keep the subwoofer off the floor or use isolation pads. This reduces vibrations that add unwanted noise to your music.
- Place acoustic panels on reflective walls
- Use bass traps in corners
- Add rugs or carpets to floors
- Use isolation pads under the subwoofer
Connecting Your Subwoofer
Connecting your subwoofer correctly is important for good sound in music production. It helps balance the low frequencies with your main speakers.
This guide covers wiring, integration with monitors, and using audio interfaces for the best setup.
Wiring And Cables
Use the right cables to connect your subwoofer. Most subs use RCA or XLR cables. Check your subwoofer and audio device for compatible connections.
- Use shielded cables to avoid noise interference.
- Keep cable length as short as possible.
- Connect the subwoofer output to the subwoofer input.
- Use balanced cables like XLR for better signal quality.
Integrating With Monitors
To blend your subwoofer with studio monitors, connect the subwoofer between the audio interface and monitors. This setup sends bass signals to the subwoofer and mid/high frequencies to monitors.
| Connection Point | Purpose |
| Audio Interface Output | Send full signal to subwoofer |
| Subwoofer Output | Pass mid/high frequencies to monitors |
| Monitors Input | Receive sound without low bass |
Using Audio Interfaces
Audio interfaces often have dedicated subwoofer outputs or multiple outputs. Use these to connect your subwoofer directly for better control.
Common audio interface subwoofer connection tips:
- Check if your interface has a low-frequency output.
- Set the interface output level to match your subwoofer.
- Use software or hardware controls to adjust crossover frequency.
- Ensure the interface outputs are balanced for clear sound.
Adjusting Subwoofer Settings
Proper subwoofer calibration is key for clear and balanced music production. Adjusting settings helps blend low frequencies with your main speakers.
This guide covers three important adjustments: crossover frequency, phase alignment, and volume level matching.
Setting Crossover Frequency
The crossover frequency decides where sound shifts from your main speakers to the subwoofer. Set it too low or too high, and you lose clarity.
- Find your main speakers’ low-frequency limit in Hertz (Hz).
- Set the subwoofer crossover 10-20 Hz above that limit.
- Use test tones or music with deep bass to check the blend.
- Adjust until bass sounds smooth and not separate from other sounds.
Phase Alignment
Phase alignment ensures the subwoofer and speakers work together without canceling each other. It fixes timing differences in sound waves.
| Phase Setting | Effect |
| 0° | Normal alignment, best if subwoofer is close |
| 180° | Reverses polarity, useful if sub is out of phase |
| Adjustable Degrees | Fine-tune to reduce bass cancellation |
Listen for the strongest bass response at the listening position. Change the phase setting and pick the one with the fullest bass.
Volume Level Matching
Volume matching balances the loudness of the subwoofer with the main speakers. Too loud or too soft bass can ruin your mix.
- Play a bass-heavy track or test tone.
- Adjust the subwoofer volume until bass feels even with other sounds.
- Use a sound level meter if possible for precise matching.
- Check in different parts of your room to confirm balance.
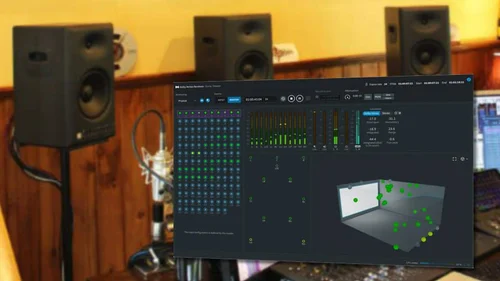
Using Measurement Tools
Calibrating subwoofers is important for clear music production. Measurement tools help you get accurate sound levels.
These tools show how your subwoofer performs in your room. This guide covers microphones, software, and reading frequency response.
Room Measurement Microphones
Room measurement microphones capture sound accurately. They help you find how your subwoofer sounds in the room.
- Use an omnidirectional microphone for even sound capture.
- Place the mic at ear level where you listen the most.
- Keep the mic still during measurements to avoid errors.
- Choose a microphone with a flat frequency response.
Software For Calibration
Calibration software analyzes sound from the microphone. It shows where your subwoofer needs adjustment.
- Room EQ Wizard (REW) is popular and free.
- Use software to generate test tones for your subwoofer.
- Look for features like real-time analysis and graphs.
- Save your calibration results for future reference.
Interpreting Frequency Response
Frequency response shows how your subwoofer plays different sounds. It helps to spot weak or too loud frequencies.
| Frequency Range | Meaning |
| 20-80 Hz | Subwoofer’s main output range |
| 80-120 Hz | Transition to main speakers |
| Peaks | Too loud at a frequency, may cause distortion |
| Dips | Frequency is too quiet or missing |

Credit: www.production-expert.com
Fine-tuning For Accuracy
Calibrating subwoofers is key for clear and balanced music production. Accurate bass helps you hear every detail in your mix.
This guide covers ways to adjust your subwoofer for better sound clarity and precision.
Equalization Techniques
Use equalization to balance the subwoofer output with other speakers. Cut or boost frequencies carefully to avoid muddiness.
- Identify problem frequencies using a test tone or sweep.
- Apply narrow cuts to reduce booming bass.
- Boost low frequencies slightly if bass sounds weak.
- Avoid extreme equalizer settings for a natural sound.
Addressing Room Modes
Room shapes and sizes create bass peaks and dips called room modes. These affect how you hear the subwoofer.
| Room Size | Common Mode Frequency | Effect |
| Small (under 10ft) | 50-100 Hz | Bass can be uneven and boomy |
| Medium (10-20ft) | 30-60 Hz | Some bass cancellation zones |
| Large (20ft+) | 20-40 Hz | More even bass, less mode issues |
Try moving the subwoofer or listening position to reduce bass problems caused by the room.
Listening Tests And Adjustments
Use your ears to check how the subwoofer sounds with music. Listen for tight bass without distortion.
- Play various tracks with strong bass elements.
- Listen for even bass response and clear low end.
- Adjust volume and equalization settings as needed.
- Repeat tests after every change to compare results.
- Ask others to listen and give feedback.
Maintaining Calibration
Keeping your subwoofers properly calibrated is key to good sound in music production. It ensures you hear bass accurately and mix well.
Regular maintenance helps your setup stay reliable. Small changes in your room or equipment can affect the sound over time.
Regular Checks
Check your subwoofers often to catch any issues early. This keeps your calibration consistent and your mixes accurate.
- Test volume levels to confirm they match your reference settings.
- Listen for distortion or rattling sounds that may signal problems.
- Inspect cables and connections for wear or damage.
- Verify that the subwoofer placement has not shifted.
- Use measurement tools to check frequency response regularly.
Adapting To Room Changes
Rooms change over time with furniture moves or new items added. These affect bass reflections and absorption.
| Room Change | Effect on Sound | Adjustment Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Adding carpets | Reduces bass reflections | Increase subwoofer level slightly |
| Moving furniture | Alters bass waves | Re-position subwoofer or recalibrate |
| Opening doors/windows | Changes room acoustics | Check frequency response again |
| Adding wall treatments | Absorbs low frequencies | Adjust crossover or gain |
Updating Settings Over Time
Over weeks and months, update your subwoofer settings to match your listening needs and room conditions.
- Measure your room response with a calibration microphone.
- Adjust crossover frequency to blend bass with main speakers.
- Set the gain level so bass is balanced, not overpowering.
- Fine-tune phase control for smooth bass wave alignment.
- Save settings and test with music you know well.
Credit: www.production-expert.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Start Calibrating Subwoofers For Music Production?
Begin by placing the subwoofer correctly in your room’s mixing space. Use measurement tools to assess frequency response and adjust crossover settings for smooth integration with main speakers.
Why Is Subwoofer Calibration Important For Mixing Accuracy?
Proper calibration ensures bass frequencies are balanced and clear. It prevents overemphasis or muddiness, helping you create mixes that translate well across different playback systems.
What Tools Are Needed For Subwoofer Calibration?
You need a calibrated microphone, room measurement software, and an SPL meter. These tools help analyze sound levels and frequency response to fine-tune your subwoofer.
How Often Should I Recalibrate My Subwoofers?
Recalibrate whenever you change room setup, move equipment, or notice sound inconsistencies. Regular checks maintain accurate bass reproduction for reliable music production.
Conclusion
Calibrating subwoofers helps you hear music clearly and accurately. It improves bass balance and fits the room’s sound better. Use simple tools and follow steps carefully for best results. Small changes make a big difference in your music. Taking time to tune your subwoofer boosts your mixing quality.
Enjoy deeper, cleaner bass that matches your production style. Keep testing and adjusting until the sound feels right. Good calibration brings your music to life and makes mixing easier.
