Imagine sitting in your living room, enveloped by rich, crystal-clear sound that makes you feel as though you’re in the middle of a concert or at the heart of an action-packed movie. Achieving this immersive experience isn’t just a fantasy; it’s within your reach.
The secret? Properly calibrating your surround sound system. Whether you’re a movie buff, a gaming enthusiast, or a music lover, understanding how to calibrate audio for surround sound can transform your home entertainment experience. But how do you ensure every note, dialogue, and sound effect hits just right?
Don’t worry, you’re about to discover simple, effective strategies to fine-tune your audio setup like a pro. Keep reading, and let’s unlock the potential of your surround sound system together.

Credit: www.theaterseatstore.com
Preparing Your Surround Sound Setup
Setting up your surround sound system correctly is key to great audio. This guide helps you prepare your space and equipment for the best sound experience.
Start by choosing the right room, placing your speakers carefully, and picking the correct gear. Each step ensures clear and balanced sound.
Choosing The Right Room
Select a room with minimal sound reflections and outside noise. A room with soft furnishings helps absorb sound and reduces echo.
- Avoid rooms with hard floors like tile or hardwood
- Choose a space with few windows and doors to limit noise
- Use curtains and rugs to soften sound reflections
- Pick a medium to large room for better speaker placement
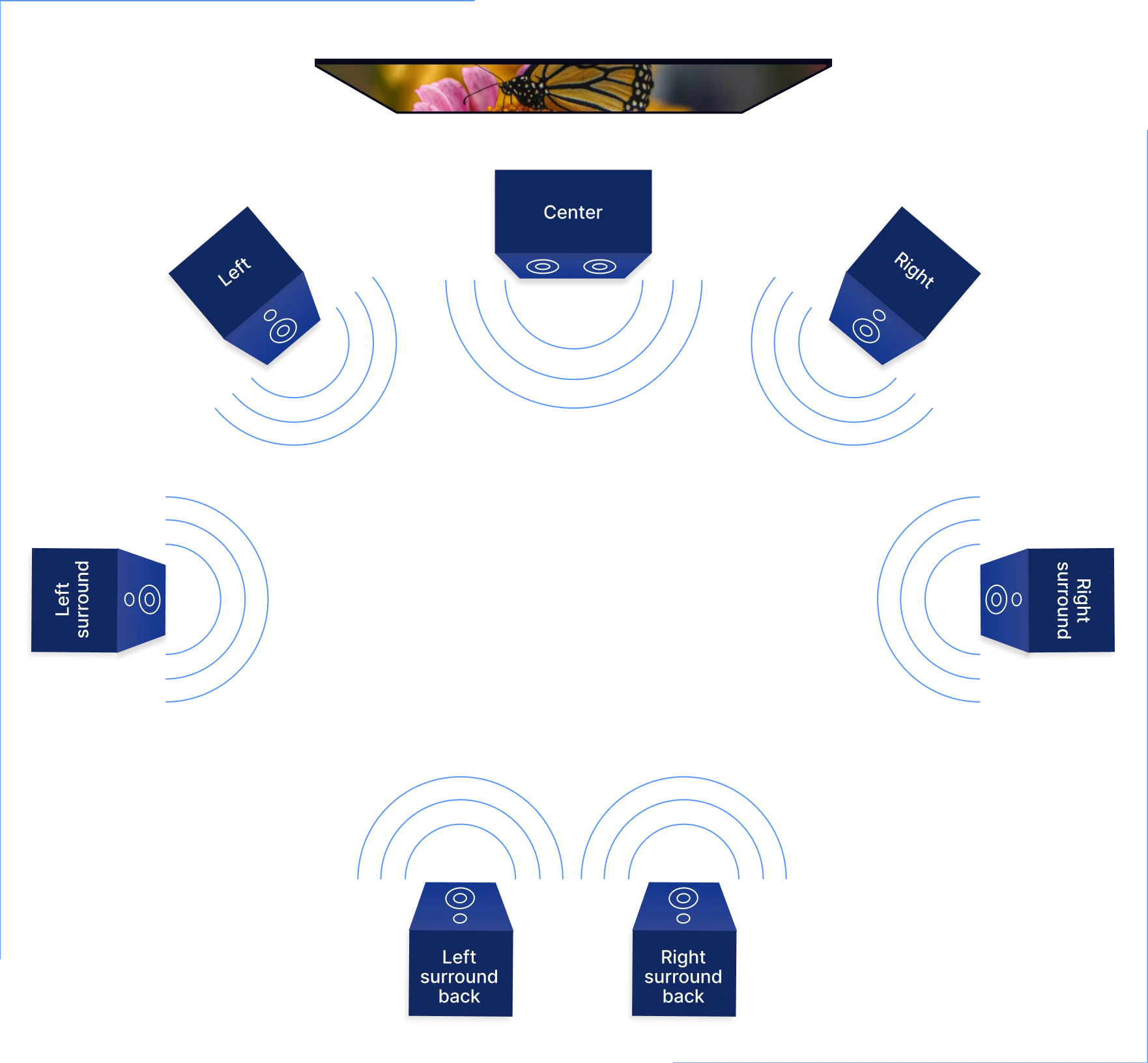
Positioning Your Speakers
Place your speakers to create an immersive sound field. Proper positioning helps each speaker deliver clear audio from all directions.
| Speaker | Placement | Height |
| Front Left and Right | At ear level, angled toward seating area | About 3 feet |
| Center | Directly above or below the TV | At ear level |
| Surround Left and Right | To the sides or slightly behind seating | 1–2 feet above ear level |
| Subwoofer | Near the front speakers or corner of room | Floor level |
Selecting The Proper Equipment
Choose equipment that matches your room size and listening habits. Quality devices improve sound clarity and system control.
Check these points when selecting your gear:
- Receiver supports your speaker setup and audio formats
- Speakers have matching power ratings
- Use high-quality cables for connections
- Consider a calibration microphone for fine tuning

Credit: www.theaterseatstore.com
Connecting And Configuring Devices
Setting up surround sound requires careful connection and configuration. Each device must be linked properly for clear audio.
This guide helps you connect your receiver, speakers, and audio source. Then, configure settings for the best sound.
Hooking Up The Receiver And Speakers
Connect each speaker to the receiver using the correct ports. Match the speaker labels to the receiver channels.
- Use speaker wires with clear polarity markings.
- Connect front left and right speakers to the front channels.
- Hook the center speaker to the center channel port.
- Attach surround speakers to the surround ports.
- Place the subwoofer and connect it via the subwoofer output.
Setting Up The Audio Source
Choose the device that sends audio to the receiver. Connect it using HDMI, optical, or coaxial cables.
| Audio Source | Connection Type |
| DVD Player | HDMI or Optical |
| Game Console | HDMI |
| TV | HDMI ARC or Optical |
| Streaming Device | HDMI |
Configuring Receiver Settings
Adjust the receiver to match your speaker setup. Use the receiver’s menu to set speaker size and distance.
- Turn on automatic speaker calibration if available.
- Set speaker sizes to small or large based on the model.
- Input the distance from each speaker to your listening spot.
- Adjust the subwoofer level for balanced bass.
- Save the settings and test the system with surround sound audio.
Measuring Sound Levels
Measuring sound levels is key to setting up surround sound. It helps balance audio across all speakers.
Accurate measurement makes sure sounds come from the right place. This improves your listening experience.
Using A Sound Level Meter
A sound level meter measures how loud each speaker is. It shows the decibel (dB) level of the sound.
Hold the meter at your listening spot. Play test tones from each speaker one by one. Adjust the speaker volume until levels match.
- Place the meter at ear level
- Use pink noise or test tones
- Measure each speaker separately
- Adjust volume to reach target dB
Utilizing Calibration Microphones
Calibration microphones capture sound from all speakers at once. They connect to your AV receiver or computer.
The microphone records test sounds and sends data to software. The software adjusts speaker levels automatically for balance.
- Place microphone at listening position
- Run the calibration program
- Let software analyze speaker output
- Apply suggested volume and delay changes
Manual Vs. Automatic Calibration
Manual calibration uses tools like sound meters. You adjust speaker volume and settings yourself. It takes more time but gives control.
Automatic calibration uses microphones and software. It is faster and easy for beginners. It may not be perfect for all rooms.
| Feature | Manual Calibration | Automatic Calibration |
|---|---|---|
| Time Required | Longer | Shorter |
| Ease of Use | Needs experience | Beginner friendly |
| Accuracy | More precise if done well | Good but varies by room |
| Equipment Needed | Sound level meter, test tones | Calibration microphone, software |
Credit: www.theaterseatstore.com
Adjusting Speaker Distances And Delays
Calibrating audio for surround sound improves your listening experience. Adjusting speaker distances and delays helps sounds reach your ears at the right time.
Proper timing creates clear and natural sound. It makes movies and music more immersive and enjoyable.
Calculating Speaker Distances
Measure the distance from your main listening position to each speaker. Use a tape measure for accuracy. Note the distance in feet or meters.
Speaker distance affects how sound waves arrive at your ears. Correct distances help your receiver adjust timing automatically.
- Start with front left and right speakers
- Measure center speaker distance
- Measure surround and rear speakers
- Record all distances for setup
Setting Delay Times
Delay time is the pause before a speaker plays sound. It matches timing with distance differences. Use your receiver’s setup menu to enter distances.
The receiver converts distance into delay time in milliseconds. Longer distances need longer delays to sync with closer speakers.
- Access your receiver’s audio setup
- Find delay or speaker distance settings
- Input measured distances for each speaker
- Save settings to apply delay times
Verifying Synchronization
Check if all speakers play sound at the same time. Play test tones or use calibration tools. Listen carefully from your main seat.
If sounds seem off or echo, adjust distances or delay settings again. Repeat the test until sounds feel balanced and clear.
- Play test tones from each speaker
- Listen for timing differences
- Adjust settings if needed
- Repeat until all sounds sync properly
Balancing Speaker Volumes
Balancing speaker volumes is key for clear surround sound. It helps create an even audio experience in your room.
This guide shows how to set levels, fine-tune speakers, and check volume consistency.
Setting Reference Levels
Start by setting a reference volume for each speaker. Use a sound meter or your receiver’s test tone.
- Play a test tone from the center speaker.
- Adjust the volume until it reaches a comfortable listening level.
- Set all other speakers to match this volume using the test tone.
- Ensure the subwoofer level matches for balanced bass.
Fine-tuning Individual Speakers
After setting reference levels, fine-tune each speaker for the best sound. Listen carefully at your main seating spot.
| Speaker | Adjustment Tip |
|---|---|
| Front Left | Increase volume if sound feels weak or unclear. |
| Front Right | Match the left speaker for even sound. |
| Surround Left | Lower volume if it overpowers dialogue. |
| Surround Right | Adjust to blend with other surround sounds. |
| Subwoofer | Raise or lower bass to avoid boominess. |
Checking Volume Consistency
Check volume consistency to avoid sudden changes. Use a list to verify key points.
- Play various surround sound content.
- Listen for any speaker that sounds too loud or quiet.
- Adjust volumes slightly as needed.
- Repeat test tones after changes.
- Make sure dialogue stays clear and balanced.
Optimizing Bass And Crossover Settings
Calibrating audio for surround sound needs careful bass and crossover settings. These settings help balance sound from all speakers.
Proper bass and crossover adjustment improves sound clarity and speaker performance. It makes your surround sound feel more natural.
Adjusting Subwoofer Placement
Subwoofer placement affects bass quality and room vibrations. Place it near a wall or corner for stronger bass.
Try different spots to find where bass sounds clear without booming or rattling. Avoid placing the subwoofer inside a cabinet.
- Start near the front speakers
- Move along the walls to test bass response
- Use a bass test tone for better judgment
- Keep the subwoofer on a solid floor surface
Setting Crossover Frequencies
Crossover frequency decides which sounds the subwoofer plays. Set it to blend bass with other speakers smoothly.
A common crossover setting is between 80Hz and 120Hz. Adjust based on your main speakers’ size and capability.
- Check your speaker specs for recommended crossover
- Set crossover lower for larger main speakers
- Raise crossover for smaller speakers that struggle with bass
- Listen for clear bass without gaps or overlaps
Controlling Bass Levels
Adjust bass volume to balance with other speakers. Too much bass can overpower sound, too little makes it weak.
Use your receiver’s bass level control or the subwoofer’s volume knob. Start at a medium level and adjust by ear.
- Play a variety of music or movie scenes
- Lower bass if it causes distortion or boominess
- Increase bass if sound feels thin or lacks depth
- Make small changes and listen carefully
Testing Surround Sound Performance
Testing your surround sound system helps ensure the best audio experience. It lets you check if all speakers work well together.
You can find problems early by testing sound. This helps fix issues before enjoying movies or music.
Playing Test Tones And Tracks
Use test tones to hear each speaker clearly. Play sounds that move from one speaker to another.
Special test tracks include sounds for front, side, and rear speakers. This shows if speakers are balanced and placed well.
- Play a tone on the front left speaker
- Listen for the same tone on the rear right speaker
- Check if the sound moves smoothly around the room
- Use calibration discs or apps with test sounds
Evaluating Soundstage And Imaging
Soundstage means where sounds seem to come from in a room. Imaging means how well you hear each instrument or voice separately.
Good soundstage and imaging make audio feel real. You can tell if sounds come from the right speaker or place.
- Listen to music with clear vocals and instruments
- Notice if sounds come from the correct speaker
- Check if sounds overlap or feel blurry
- Adjust speaker position if sounds seem off
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If sound is missing or low from some speakers, check connections first. Loose wires cause many problems.
Other issues include echoes, delays, or uneven volume. Fix these by adjusting speaker distance and settings.
- Check all speaker cables and plugs
- Use your receiver’s calibration tool
- Move speakers closer or farther from walls
- Lower volume on speakers that sound too loud
- Reset settings if sound feels strange after changes
Maintaining Calibration Over Time
Calibrating your surround sound system is important for great audio. Keeping this calibration over time ensures you get the best sound quality.
Small changes in your system or room can affect how sound works. Regular care helps maintain clear and balanced audio.
Scheduling Regular Checks
Set a schedule to check your audio calibration often. This keeps your sound system working well as time passes.
Check your system every few months or after moving any speakers. Regular tests catch problems early and keep sound clear.
- Test speaker levels and distances
- Check for changes in sound balance
- Use calibration tools or apps
- Note any odd sounds or distortions
Updating Firmware And Software
Audio devices often get updates from the maker. These updates fix bugs and improve sound performance.
Keep your receiver and calibration tools up to date. This helps keep your system running smoothly and accurately.
- Check for firmware updates on your receiver
- Update calibration microphones or apps
- Follow instructions carefully during updates
- Restart devices after updating
Adapting To Room Changes
Your room affects how sound travels. Changes like new furniture or decorations can shift audio quality.
Recalibrate your system if you change your room. Adjust speaker placement and settings to fit the new space.
- Move speakers if furniture blocks sound
- Re-run calibration after room changes
- Use acoustic panels if needed
- Keep the listening area clear
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Best Way To Calibrate Surround Sound Audio?
Use a sound level meter or calibration microphone for precise measurements. Adjust speaker levels, distances, and crossover frequencies. Follow your AV receiver’s setup guide for accurate surround sound balance and optimal audio performance.
How Often Should I Calibrate My Surround Sound System?
Calibrate your system every 6 to 12 months. Recalibrate after moving speakers or changing room layout. Regular calibration ensures consistent audio quality and an immersive surround sound experience.
Can I Calibrate Surround Sound Without Special Equipment?
Yes, you can use built-in AV receiver test tones. However, professional calibration tools provide more accuracy. For best results, use a calibration microphone and sound meter with your receiver’s auto setup.
Why Is Speaker Distance Important In Surround Sound Calibration?
Correct speaker distance ensures sound reaches the listener simultaneously. This improves audio timing and clarity. Accurate distance settings create a balanced and immersive surround sound experience.
Conclusion
Calibrating your surround sound improves your listening experience. It balances audio levels and makes sounds clear. Use a sound meter or calibration tool for best results. Adjust speaker positions and settings carefully. Test the system by playing different audio types.
Small changes can make a big difference. Enjoy movies, music, and games with better sound. Regular calibration keeps your system working well. Take time to fine-tune and hear every detail. Surround sound feels more natural and immersive this way.
